01 - Android Intro
Topics
- Android overview
- Basic Android Studio usage
- Kotlin language
- UI creation
- App lifecycle and state
- Local storage and data access (SQLite)
- Sensors (proximity, geomagnetic, motion, GPS, …)
- Web services (REST API)
- Modern architecture
Android
Operating system, devised for mobile equipment (mostly)
Usage: phones, tablets, TV-s, watches, glasses, cars, laptops, cameras, game consoles, …
Market share among smartphones – ca 85% (iOS 14%)
Open-source project
Google apps and services are closed source (mail, map, etc.)
History
- 2003 – founded (lead: Andy Rubin)
- Initial idea – OS for cameras
- New plan – Mobile OS, (others: Symbian/Nokia and Win Mobile)
- 2005 – Google acquires the whole project
- 2007 – Open Handset Alliance
- Google, HTC, Sony, Samsung, Dell, Motorola, LG, Qualcomm, Intel, etc…
- 2008 – Android 1.0 (HTC Dream, no touchscreen)
- 2009 – Android 1.5 Cupcake (iPhone 2007, iPhone 3G 2008)
- 2010 – Android 2.2 Froyo, 2.3 Gingerbread
- 2011 – Android 3.0 Honeycomb (tablets only)
- 2011 - Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich
- HOLO UI
- 2014 - Android 5 Lollipop
- Material design
- Dalvik vs ART (Android Runtime) (JIT or precompile, garbage collection)
- 2015 - Android 6 Marshmallow
- 2016 – Android 7 Nougat
- 2017 – Android 8 Oreo
- 2018 – Android 9 Pie
- 2019 – Android 10 Q – moves closer to iOS, security clamped down
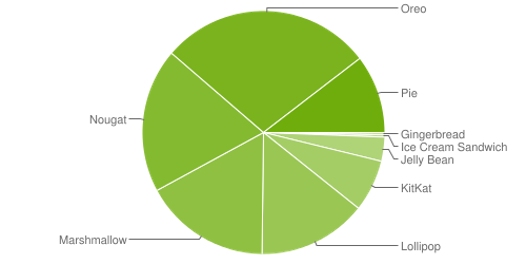
Version distribution
2020
- Pie – 9.X – 10%
- Oreo – 8.X – 28%
- Nougat – 7.X - 19%
- Marshmallow – 6.X – 17%
- Lollipop - 5.X – 14%
- KitKat – 4.4 – 7%
- 4.4 and higher - ca 95%
Latest info (2024 fall)
- 22 LolliPop 99.6%
- 24 Nougat 98.8%
- 27 Oreo 93.9%
- 28 Pie 89.6%
- 29 Android 10 81.2%
- 30 Android 11 67.6%
- 31 Android 12 48.6%
- 33 Android 13 33.9%
- 34 Android 14 13.0%
Latest info (2025 fall)
- 22 LolliPop 99.8%
- 24 Nougat 98.6%
- 27 Oreo 96.1%
- 28 Pie 93.4%
- 29 Android 10 87.6%
- 30 Android 11 77.4%
- 31 Android 12 61.5%
- 33 Android 13 48.7%
- 34 Android 14 31.9%
- 35 Android 15 4.5%
- 36 Android 16 <1%
Android Architecture
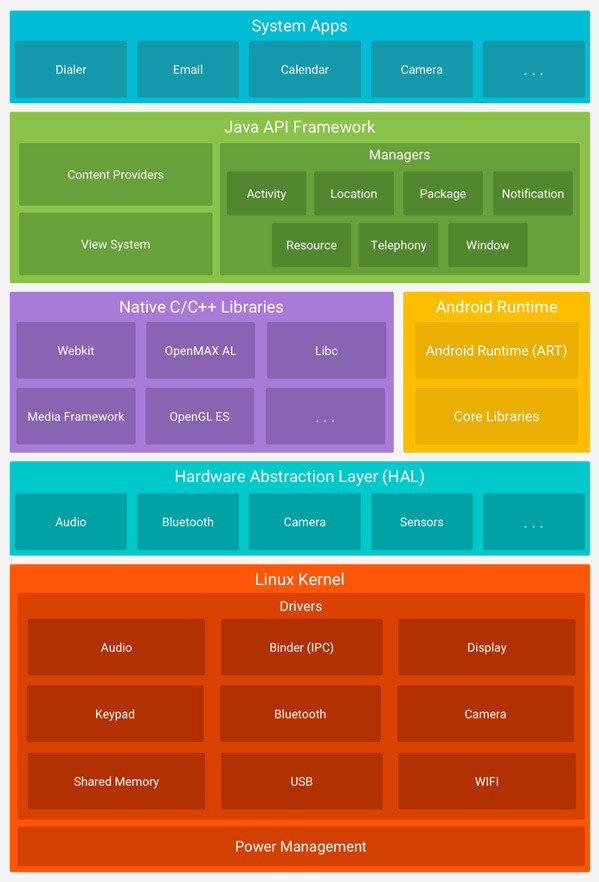
App types
- NDK - C/C++
- Close to hardware and operating system
- SDK - Native <- this course!!!!
- Kotlin/Java (ART/Dalvik), using system libraries
- Hybrid – React Native, Ionic, etc.
- Cross platform – Xamarin (C#), Flutter (Dart), React Native, etc.
- Html/JS – Progressive Web Apps
- One codebase/layout for different platforms
- Problems with UI, weak access to hardware
- There is also course on Hybrid Mobile Apps - ICD0018 (fall semester)
App architecture - AndroidManifest.xml
- The manifest file presents essential information about your app to the Android system, information the system must have before it can run any of the app's code.
- Describes the components of the application — the activities, services, broadcast receivers, and content providers that the application is composed of.
- Declares which permissions the application must have in order to access protected parts of the API and interact with other applications.
- Declares hardware requirements.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:dataExtractionRules="@xml/data_extraction_rules"
android:fullBackupContent="@xml/backup_rules"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Test01"
tools:targetApi="31">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
App architecture - build.gradle (app)
- Declares the minimum level of the Android API that the application requires (minSdk).
- Additional libraries (dependencies)
plugins {
alias(libs.plugins.android.application)
alias(libs.plugins.kotlin.android)
}
android {
namespace = "ee.taltech.test01"
compileSdk = 34
defaultConfig {
applicationId = "ee.taltech.test01"
minSdk = 27
targetSdk = 34
versionCode = 1
versionName = "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner = "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
isMinifyEnabled = false
proguardFiles(
getDefaultProguardFile("proguard-android-optimize.txt"),
"proguard-rules.pro"
)
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = "1.8"
}
}
dependencies {
implementation(libs.androidx.core.ktx)
implementation(libs.androidx.appcompat)
implementation(libs.material)
implementation(libs.androidx.activity)
implementation(libs.androidx.constraintlayout)
testImplementation(libs.junit)
androidTestImplementation(libs.androidx.junit)
androidTestImplementation(libs.androidx.espresso.core)
}
App code
- MainActivity.kt
package ee.taltech.test01
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.core.view.ViewCompat
import androidx.core.view.WindowInsetsCompat
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
enableEdgeToEdge()
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(findViewById(R.id.main)) { v, insets ->
val systemBars = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars())
v.setPadding(systemBars.left, systemBars.top, systemBars.right, systemBars.bottom)
insets
}
}
}
- actvity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello World!"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
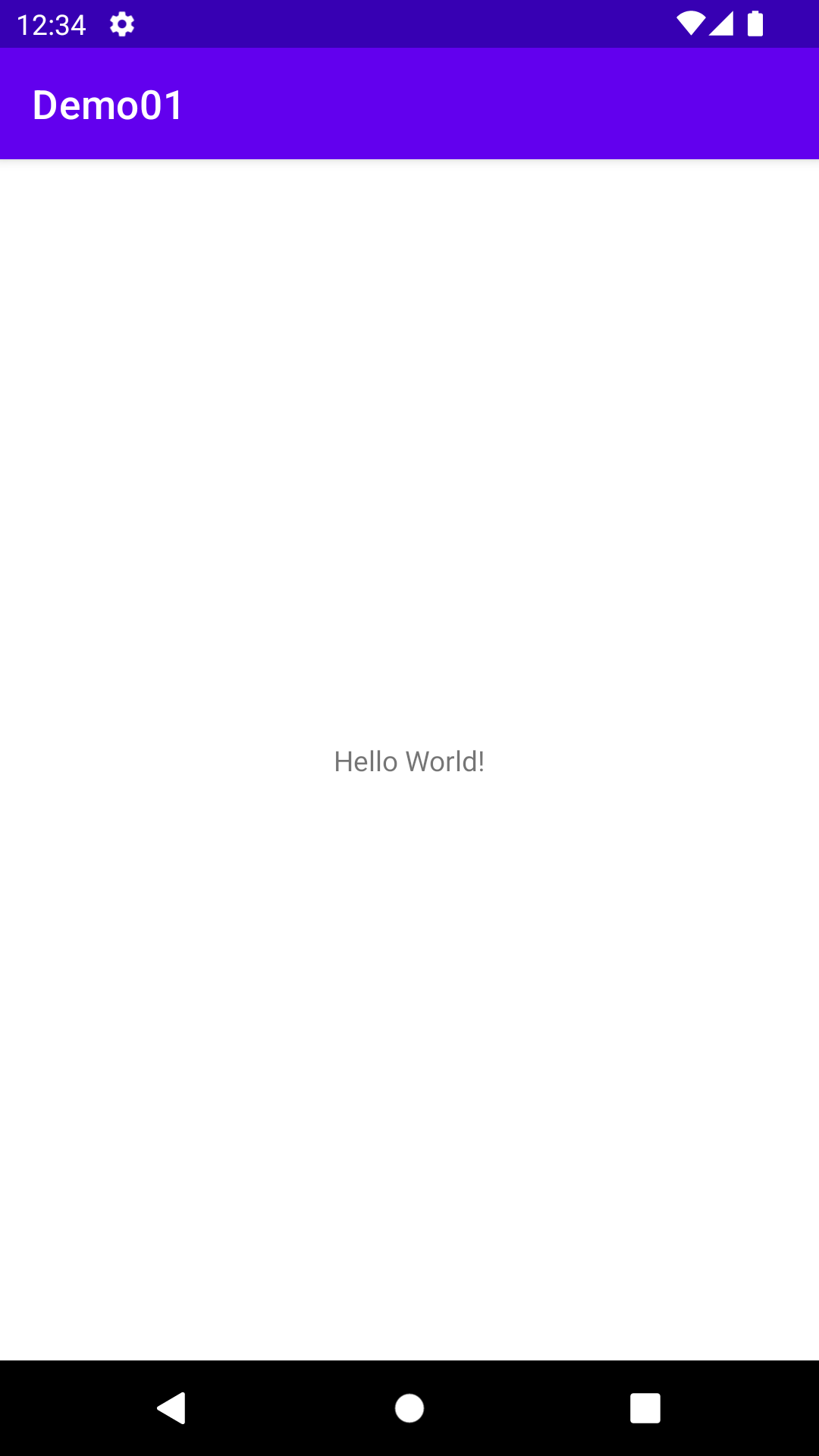
- UI generated from XML
Other resources
- Images
- Animations
- Menu
- Strings
- Misc files
APK
- Android Application Package
- ZIP file, combines all the resources and java bytecode
- Signed with developer key
- Developer key must be the same from version to next version
- Don’t lose your keys (passwords)
- Android Studio takes care of APK creation
- APK-s can be downloaded from store, using 3-rd party utilities
- Resources can be used as is
- Most elements/code can be decompiled/recompiled
Google Play - app store
- Almost no review process
- Problems are dealt with afterwards
- App hijacking, etc. are real problems
App security
- Every app works in its own private virtual machine (Zygote)
- Need permission for system resources/hardware
- confirmed on app install
- reconfirmed when app has not been used for some time
- Data is private, no other app can access directly other app data
- Everything is possible on rooted device
- End user is the weakest link
Developer problems
- Gazillion different hardware devices and capabilities
- Lots of different Android implementations
- Samsung TouchWiz
- HTC Sense
- ...
- Migration to newer versions very slow (or not done at all)
- Rooted phones
- Ca 2X time spent on development compared to iOS
- Ca 60% better income on iOS
Testing on devices


Device variability


Other hardware



Hands on demo time - Notes
findViewById vs
Add kotlin-android-extensions to build.gradle (deprecated) for initial view elemnts to code binding.
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
id 'kotlin-android'
}
apply plugin: 'kotlin-android-extensions'
Remove virtual keyboard from screen when done with it
fun buttonGreetClicked(view: View) {
textViewGreeting.text = "Hello, " + editTextName.text + "!"
val inputMethodManager = getSystemService(INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE) as InputMethodManager
inputMethodManager.hideSoftInputFromWindow(getCurrentFocus()?.windowToken, 0)
}