09 - Razor Pages - Views
Passing data
Loosely typed (ViewData)
- ViewData - collection of data
- Accessible both in code and in views
- ViewData – string keys based dictionary (
Dict<string,object>) ViewData["key"] = someObject;
- ViewData – string keys based dictionary (
- No intellisense support, needs casting (except strings)
Razor Syntax
- Razor is markup syntax for embedding server based code into web pages.
- Razor syntax – Razor markup, C# code and HTML
- Default language in razor is HTML
@symbol is used to transition from HTML into C#- Razor expressions – any output is rendered to html output
- Implicit – generally spaces are not allowed
<div>@DateTime.Now</div>
<div>@DoSomething("Hello", "World")</div> - Explicit - @(…C#...) - spaces are ok
<div>@(DateTime.Now - TimeSpan.FromDays(7))</div
- Implicit – generally spaces are not allowed
Expression encoding
- C# expressions in Razor are converted to string (
.ToString()) and html encoded - If C# expressions evaluates to
IHtmlContent, then it is not encoded and rendered directly - Use html Raw helper to write out unencoded content
@Html.Raw("<span>Hello World</span>")
Razor code blocks
-
@{ … c# statement; .... }
-
Default language in code block is C#
-
Using html inside code block transitions language back to html
-
Explicit transition to html
- Use razor
<text></text>tags
@{ var inCSharp = true;
<p>Now in HTML, was in C# @inCSharp</p>
}- Single line transition -
@:
@for (var i = 0; i < people.Length; i++) { var person = people[i]; @:Name: @person.Name } - Use razor
Control structures
Conditionals
@if, else if, else
@switch
@if (value % 2 == 0) {
<p>The value was even</p>
} else if (value >= 1337) {
<p>The value is large.</p>
} else {
<p>The value was not large and is odd.</p>
}
Looping
@for
@foreach
@while
@do while
Comments
Razor supports C# and HTML comments.
@{ /* C# comment. */ // Another C# comment. }
<!-- HTML comment -->
Razor comments @* …. *@
@* @{ /* C# comment. */ // Another C# comment. }
<!-- HTML comment -->
*@
Razor view directives
A directive will typically change the way a page is parsed or enable different functionality within your Razor page.
@page
@using
@model
@inherits
@inject
@functions
@section
@using, @model, @inject, @section
@using System.IO
adds using to the generated code@model SomeModelType
public class _Views_Test_cshtml : RazorPage< SomeModelType>@inject
Enables you to inject a service from your service container into your Razor page for use@section
Used in conjunction with the layout page to enable views to render content in different parts of the rendered HTML page
@function
@functions { // C# Code }
@functions { public string GetHello() { return "Hello"; } }
<div>From method: @GetHello()</div>
Layout
Most web apps have a common layout that provides the user with a consistent experience as they navigate from page to page.
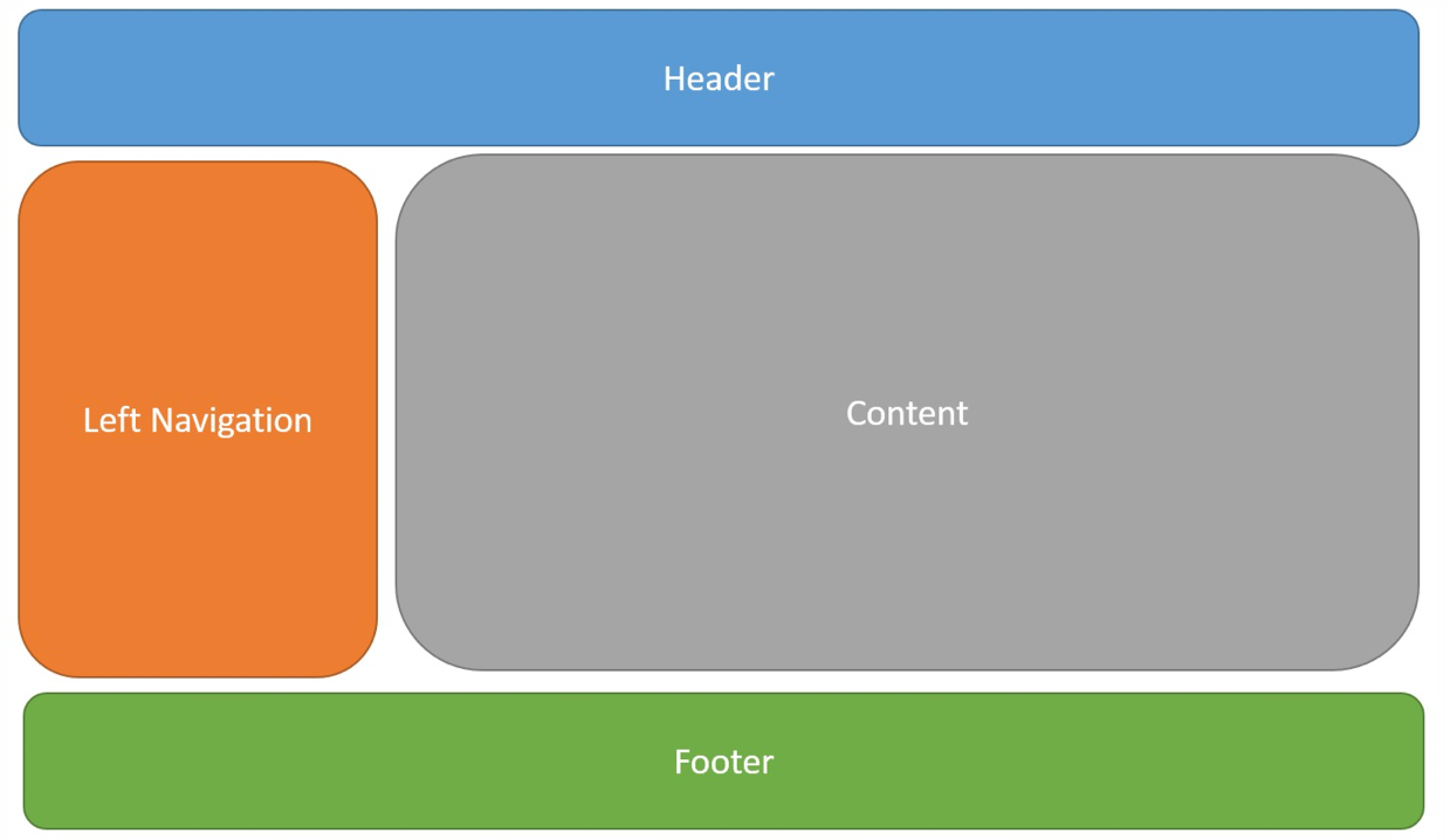
Razor pages layout
-
Default layout is located at
Pages\Shared\_Layout.cshtml -
Specifying an layout
- Can use partial name or full path
@{ Layout = "_Layout"; } -
Every layout must call
RenderBody()
WhereverRenderBody()is called, contents of the view will be rendered.
Section
Defining placeholder in layout file @RenderSection("Scripts", required: false)
Then define the section in view:
@section Scripts { @{await Html.RenderPartialAsync("_ValidationScriptsPartial");} }
Shared directives
Directives can be placed in file _ViewImports.cshtml.
Supports only these:
@addTagHelper@removeTagHelper@tagHelperPrefix@using@model@inherits
@using WebApp
@using WebApp.Models.AccountViewModels
@using WebApp.Models.ManageViewModels
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity
@addTagHelper *, Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.TagHelpers
Pages\_ViewImports.cshtml is shared location for all views.
Initial code
- Place initial code in
_ViewStart.cshtml - Included in front of every page
- Hierarchical, like
_ViewImports - These are included in order, starting from the
/Pages
@{
Layout = "_Layout";
}
Partial views
A partial view is a view that is rendered within another view. The HTML output generated by executing the partial view is rendered into the calling (or parent) view.
Partial views do not include _ViewStart.cshtml
Calling an partial view (returns an IHtmlString):
@Html.Partial(“_SomePartialView")@await Html.PartialAsync("_SomePartialViewWithAsyncCode")<partial name="_PartialName" />
Referencing
// Uses a view in current folder with this name
// If none is found, searches the Shared folder
@Html.Partial("ViewName")
// A view with this name must be in the same folder
@Html.Partial("ViewName.cshtml")
// Locate the view based on the application root
// Paths that start with "/" or "~/" refer to the application root
@Html.Partial("~/Pages/Folder/ViewName.cshtml")
@Html.Partial("/Pages/Folder/ViewName.cshtml")
// Locate the view using relative paths
@Html.Partial("../Account/LoginPartial.cshtml")
Accessing data
- Receives a copy of parents ViewData (not persisted)
- You can pass an instance of ViewDataDictionary
@Html.Partial("PartialName", customViewData) - You can pass an ViewModel (declared with @model in partial)
@Html.Partial("PartialName", Model.ContactType) - You can pass both an ViewModel and an instance of ViewDataDictionary
@Html.Partial("ArticleSection", sectionModel, new ViewDataDictionary(this.ViewData) { { "index", index } }) - You can create new ViewDataDictionary and include existing viewData into it
new ViewDataDictionary(this.ViewData) { { "index", index } }
Tag helpers
- Tag Helpers enable server-side code to participate in creating and rendering HTML elements in Razor files.
- There are many built-in Tag Helpers for common tasks - such as creating forms, links, loading assets and more - and even more available in public GitHub repositories and as NuGet packages.
- Tag Helpers are authored in C#, and they target HTML elements based on element name, attribute name, or parent tag.
- Tag helpers do not replace Html helpers – there is not a Tag helper for every Html helper.
<form> helpers #1
asp-all-route-dataasp-antiforgeryasp-fragmentasp-pageasp-route-<parameter name>
<form
asp-page="SomeOtherPage"
asp-route-returnurl="@ViewData["ReturnUrl"]"
method="post"
class="form-horizontal">
<form method="post" class="form-horizontal" action="/Account/Login"></form>
<form> helpers #2
Asp-page="<Page Name>"
Forms target is constructed out of pageAsp-route-<parameter name>
Parameter name is added to forms target (as query string)Asp-antiforgery="true/false"
Generate anti-forgery token as hidden value to form.Usually controlled by [ValidateAntiForgeryToken] attribute in Controller
<input
name="__RequestVerificationToken"
type="hidden"
value="CfDJ8O3e77kPeG5Fju-exRwNp8_5FUhPiQ-vxSyhpobWy0ORwL1QWwrZfyGSKxe-hClHCByTfSImSXgBIJ-cxSgHrvQsOLluGSIwgAFHclMpAIWaBBB8csOoiW0gS1o_bp_sQlhxrypM37B47MU8I_cfN1A"
/>
<form> helpers #3
Asp-all-route-data
Give a dictionary for all route/target parametersAsp-fragment
add#<value>to route/target
<div>
Asp-validation-summary– display validation summary in this divValidationSummary.All– property and modelValidationSummary.ModelOnly– only modelValidationSummary.None- none
<input> helpers #1
Asp-for="<ModelExpression>"- Generates id and name attributes – used later in model binding
- Sets the type attribute – based on model type and data annotations
- Sets up client side validation
asp-for="property1"becomes in generated codem=>m.property1
Asp-format="<format>"- Use to format value
<input asp-for="SomeNumber" asp-format="{0:N4}"/>
- Use to format value
- Input tag helper does not handle collections and templates – use Html.XxxxxFor
<input> helpers #2
Input type is set based on .NET type.
| .NET type | Input type |
|---|---|
| Bool | type="checkbox" |
| String | type="text" |
| DateTime | type="datetime" |
| Byte | type="number" |
| Int | type="number" |
| Single, Double | type="number" |
<input> helpers #3
Or use data annotations.
| Attribute | Input type |
|---|---|
| [EmailAddress] | type="email" |
| [Url] | type="url" |
| [HiddenInput] | type="hidden" |
| [Phone] | type="tel" |
| [DataType(DataType.Password)] | type="password" |
| [DataType(DataType.Date)] | type="date" |
| [DataType(DataType.Time)] | type="time" |
<span>
Asp-validation-for
Display validation error (if there is one for this model property) in this span
<span asp-validation-for="LastName" class="text-danger"></span>
<label>
Asp-for
Generate label for this model property
<label asp-for="LastName" class="col-md-2 control-label"></label>
<label class="col-md-2 control-label" for="FirstName">FirstName</label>
<textarea>
Asp-for
Generate textarea input for this model property. Id, name, validation
<select>
-
Asp-for
specifies the model property -
Asp-items
sepcifies option elements (List<SelectListItem>)<select asp-for="Country" asp-items="Model.Countries"></select> -
You can generate option list from enums
<select asp-for="EnumCountry" asp-items="Html.GetEnumSelectList<CountryEnum>()"></select>
option group <optgroup>
The HTML <optgroup> element is generated when the view model contains one or more SelectListGroup objects.
public CountryViewModelGroup()
{
var NorthAmericaGroup = new SelectListGroup { Name = "NA" };
var EuropeGroup = new SelectListGroup { Name = "EU" };
Countries = new List<SelectListItem>{
new SelectListItem{
Value = "MEX",
Text = "Mexico",
Group = NorthAmericaGroup
},
new SelectListItem{
Value = "FR",
Text = "France",
Group = EuropeGroup
},
...
<select> multi-select
The Select Tag Helper will automatically generate the multiple = "multiple" attribute if the property specified in the asp-for attribute is an IEnumerable
public class CountryViewModelIEnumerable
{
public IEnumerable<string> CountryCodes { get; set; }
public List<SelectListItem> Countries { get; } = new List<SelectListItem>
{
new SelectListItem { Value = "MX", Text = "Mexico" },
new SelectListItem { Value = "CA", Text = "Canada" },
...
Collections
public class ToDoItem
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public bool IsDone { get; set; }
}
@model List<ToDoItem>
@for (int i = 0; i < Model.Count; i++) {
<tr>
<td>
<label asp-for="@Model[i].Name"></label>
</td>
<td>
<input asp-for="@Model[i].IsDone" />
</td>
</tr>
}</ToDoItem
>
<a>
Asp-page,Asp-route-<parameter name>Asp-host
Specify host to use in generated link (default is relative to current host)Asp-protocol
Specify protocol to use (default is current protocol)
<img>
Asp-append-version="<true/false>"
Enable cache busting. Generates file version hash and appends it to source.
<script> helpers #1
<script
src="https://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jquery/jquery-2.2.0.min.js"
asp-fallback-src="~/lib/jquery/dist/jquery.min.js"
asp-fallback-test="window.jQuery"
crossorigin="anonymous"
integrity="sha384-K+ctZQ+LL8q6tP7I94W+qzQsfRV2a+AfHIi9k8z8l9ggpc8X+Ytst4yBo/hH+8Fk"
></script>
Asp-append-versionAsp-fallback-srcAsp-fallback-src-excludeAsp-fallback-src-includeAsp-fallback-testAsp-src-excludeAsp-src-include
<script> helpers #2
Asp-append-versionAsp-fallback-src
If asp-fallback-test is negative (no network) then fall back to this locationAsp-fallback-test
Javascript functionality to testAsp-fallback-src-exclude,Asp-fallback-src-include,Asp-src-exclude,Asp-src-include
Comma separated list of sources to include or exclude
<link>
Asp-append-versionAsp-fallback-hrefAsp-fallback-href-excludeAsp-fallback-href-includeAsp-fallback-test-classAsp-fallback-test-propertyAsp-fallback-test-valueAsp-href-excludeAsp-href-include
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://…/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css"
asp-fallback-href="~/lib/css/bootstrap.min.css"
asp-fallback-test-class="sr-only"
asp-fallback-test-property="position"
asp-fallback-test-value="absolute"
/>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/css/site.min.css" asp-append-version="true" />
<environment>
Names=“comma_separated_list"
asp.net core pre-defines following enviroments –Development,Staging,Production. Useful for branching in cshtml files.
<environment names="Development">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/css/site.css" />
</environment>
<environment names="Staging,Production">
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/…/css/bootstrap.min.css"
asp-fallback-href="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"
asp-fallback-test-class="sr-only"
asp-fallback-test-property="position"
asp-fallback-test-value="absolute"
/>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/css/site.min.css" asp-append-version="true" />
</environment>
HTML helpers
- Tag helpers are there in addition to Html helpers.
- Some functionality is only possible with Html helpers.
- Html helpers generate full html tags – harder to read cshtml files, designers cant modify easily
- Four main categories of helpers
- Output
- Input
- Form
- Link
Output
DisplayForDisplayForModelDisplayNameForDisplayNameForModelDisplayTextForLabelForLabelForModel
Input
EditorForTextAreaForTextBoxForDropDownForEnumDropDownForListBoxForRadioButtonForHiddenForCheckBoxForPasswordFor
Form
BeginFormBeginRouteFormEndFormAntiForgeryTokenHiddenFor
Link
ActionLinkRouteLink
EditorFor
-
EditorFor(expression) -
EditorFor(expression, additionalViewData) -
EditorFor(expression, templateName) -
EditorFor(expression, templateName, additionalViewData) -
EditorFor(expression, templateName, htmlFieldName) -
EditorFor(expression, templateName, htmlFieldName, additionalViewData) -
Expression - lambda
<dt>@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.FirstName)</dt>
<dd>@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.FirstName)</dd>
@Html.EditorFor( model => model.Participant.FirstName, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } } )
@Html.ValidationMessageFor( model => model.Participant.FirstName, "", new { @class = "text-danger" } ) @Html.ActionLink("Show items",
"Show", new { id = 1}, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "btn btn-primary", role = "button" })
Named Handler Methods
asp-page-handler
Enables you to specify multiple methods that can be executed for a single verb. You might want to do this if your page features multiple forms, each one responsible for a different outcome, for example
<div class="row">
<div class="col-lg-1">
<form asp-page-handler="edit" method="post">
<button class="btn btn-default">Edit</button>
</form>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-1">
<form asp-page-handler="delete" method="post">
<button class="btn btn-default">Delete</button>
</form>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-1">
<form asp-page-handler="view" method="post">
<button class="btn btn-default">View</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
OR
Form with multiple different actions.
<form method="post">
<button asp-page-handler="Register">Register Now</button>
<button asp-page-handler="RequestInfo">Request Info</button>
</form>
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostRegisterAsync()
{
//…
return RedirectToPage();
}
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostRequestInfo()
{
//…
return RedirectToPage();
}
All this will add ?handler=somehandler to url submitted to server. Asp.net core chooses correct method based on HTTP verb and handler value.
If you prefer not to have query string values representing the handler's name in the URL, you can use routing to add an optional route value for "handler" as part of the route template in the @page directive:
@page "{handler?}"